- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

- Intuitive search with relevant results
- Easily compare products in detail
- Quick, simple checkout
- Be part of our community, read or submit product reviews
We would love to know what you think, so we have included a feedback tab on every page.
 Biochemicals
Biochemicals
- Autophagy
- Cell Cycle/Checkpoint
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Chromatin/Epigenetic
- Endocrinology/Hormones
- Hedgehog/Smoothened
- Angiogenesis
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair
- Apoptosis
- NF-κB
- Neuroscience
- MAPK
- Microbiology/Virology
- GPCR/G Protein
- TGF-beta/Smad
- Immunology/Inflammation
- Proteases/Proteasome
- Stem Cells
- Ubiquitination
- Oxidation-Reduction
- Membrane transporter/Ion channel
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling
- Metabolism
- Wnt/beta-catenin
- JAK/STAT signaling
- Tyrosine Kinase/Adaptors
- TLR
- PARP
- Antibody-drug Conjugate/ADC Related
- Focused Bioactive LibrariesApproved Drug LibraryFDA-Approved Drug LibraryFDA-Approved & Pharmacopeia Drug LibraryClinical Compound LibraryPreclinical Compound LibraryBioactive Compound LibraryTarget-Focused Phenotypic Screening LibraryReFRAME Related LibraryEpigenetics Compound LibraryCytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound LibraryTranscription Factor-Targeted Compound LibraryGPCR Compound LibraryIon Channel Inhibitor LibraryEndocrinology-Hormone Compound LibraryJAK-STAT Compound LibraryNF-κB Signaling Compound LibraryDNA Damage & Repair Compound LibraryUbiquitination Compound LibraryFerroptosis Compound LibraryCuproptosis Compound LibraryKinase Inhibitor LibraryAnti-Cancer Compound LibraryAnti-Bacterial Compound LibraryAnti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound LibraryCNS-Penetrant Compound LibraryAnti-Viral Compound LibraryAnti-Neurodegenerative Disease Compound LibraryPeptide Compound Library
- Natural Product LibrariesNatural Product Library for HTSNatural Product LibraryHuman Endogenous Metabolite LibraryHuman Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library PlusNatural Product Derivatives LibraryPolyphenolic Natural Product LibraryAlkaloid Natural Product LibraryFlavonoid Natural Product LibraryTerpene Natural Product LibraryCovalent Natural Product LibraryThe Yao nationality medicine LibraryTibetan medicine Compound LibraryTraditional Mongolian Medicine Compound LibraryFood as Medicine Compound LibraryMarine Natural Product LibraryMicrobial Natural Product LibraryAnti-infective Natural Product LibraryAnti-Tumor Natural Product LibraryAnti-Inflammatory Traditional Chinese Medicine Compound LibraryAnti-COVID-19 Traditional Chinese Medicine Compound LibraryAnti-virus Traditional Chinese Medicine Monomer LibraryAnti-Colorectal Cancer Traditional Chinese Medicine Compound LibraryPBCRBS Traditional Chinese Medicine Compound LibraryTraditional Chinese Medicine Monomer LibrarySelected Plant-Sourced Compound LibraryGut Microbial Metabolite LibrarySelectable Natural Product LibraryNatural Product Derivatives Library for CADD
- Fragment LibrariesHigh Solubility Fragment LibraryDrug-Fragment Library
- Drug-like Compound LibrariesMini Scaffold LibraryGolden Scaffold LibrarySmartTM LibraryDiversity Core Library Part1Covalent Inhibitor LibraryDrug-like natural compound library
- Steroids
- Coumarins
- Lignans
- Saccharides and Glycosides
- Alkaloids
- Terpenoids
- Phenylpropanoids
- Flavonoids
- Phenols
- Quinones
- Others
- CAR-T Therapy Target Proteins
- CD Proteins
- Complement System
- Cytokines and Growth Factors
- Enzymes
- Fluorescent Proteins
- Hormones
- Immune Checkpoint Proteins
- Others
- Receptor Proteins
- Viral Proteins
- Molecular Docking
- Virtual Screening
- Biomolecular Interaction
- Custom Synthesis
- AI-driven Ultra High-throughput Virtual Screening
- Tumor/Cancer
- Immune and Inflammatory
- Neurodegenerative Diseases
- Endocrine and Metabolism
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Infectious Diseases
- Organoids and Stem Cells
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail
- Deacetylase Inhibitor Cocktail
- RIPA Lysis Buffer
- BCA Protein Quantification Kit
- Sterile Antibiotic Solution
- Magnetic Beads
- Immunoprecipitation Beads
- Immunoprecipitation Kits
- Streptavidin Magnetic Beads
- Protein Purification Magnetic Beads
- Cell Isolation Kits
- Preactivated Magnetic Beads
- Polymer Magnetic Beads
- Agarose Magnetic Beads
- Dextran Magnetic Beads
- Agarose Beads
- Inhibitory Antibodies
- Peptides
- PROTAC
- E3 Ligase Ligand-Linker Conjugate
- Ligand for E3 Ligase
- Ligand for Target Protein for PROTAC
- Linker
- PROTAC Selection
- PROTAC-linker Conjugate for PAC
- SNIPER
- Target Protein Ligand-Linker Conjugate
- dyes
- Isotope products
- Deuterium Labeled Compounds
- Carbon-13 Labeled Compounds
- Nitrogen-15 Labeled Compounds
- Antibodies
- Primary antibodies








- ALK
- Bcr-Abl
- BTK
- EGFR
- FAK
- FGFR
- FLT
- HER
- HIF
- JAK
- PDGFR
- Src
- Syk
- VDA
- VEGFR
- Apoptosis
- ASK
- BCL
- Caspase
- c-RET
- DAPK
- Fas/FasL
- Ferroptosis
- FKBP
- FOXO1
- IAP
- Mdm2
- Necroptosis
- OXPHOS
- p53
- PD-1/PD-L1
- PERK
- Pyroptosis
- RIP kinase
- Survivin
- TNF
- Autophagy
- CXCR
- FKBP
- LRRK2
- lysosomal autophagy
- Mitophagy
- Antifolate
- APC
- Aurora Kinase
- BMI-1
- CDK
- Cell Cycle Arrest
- Chk
- c-Myc
- DHFR
- DNA/RNA Synthesis
- DUB
- DYRK
- Haspin Kinase
- IRE1
- KSP
- LIM Kinase
- Nucleoside Antimetabolite/Analog
- PD-1/PD-L1
- PLK
- Rho
- ROCK
- Serine/threonin kinase
- Wee1
- AMPK
- Aurora Kinase
- DNA Methyltransferase
- Epigenetic Reader Domain
- HDAC
- HIF
- HIF/HIF Prolyl-Hydroxylase
- Histone Acetyltransferase
- Histone Demethylase
- Histone Methyltransferase
- HuR
- JAK
- Methionine Adenosyltransferase (MAT)
- PAD
- PARP
- Pim
- PKC
- Sirtuin
- Akt
- Arp2/3 Complex
- Bcr-Abl
- Dynamin
- FAK
- Gap Junction Protein
- HSP
- Integrin
- Kinesin
- Microtubule Associated
- Myosin
- PAK
- PKC
- ROCK
- Wnt/beta-catenin
- ATM/ATR
- BMI-1
- CRISPR/Cas9
- DHFR
- DNA
- DNA Alkylation
- DNA Alkylator/Crosslinker
- DNA gyrase
- DNA/RNA Synthesis
- DNA-PK
- DUB
- HDAC
- MTH1
- Nucleoside Antimetabolite/Analog
- PARP
- PPAR
- Sirtuin
- Telomerase
- Topoisomerase
- Androgen Receptor
- Aromatase
- Estrogen Receptor/ERR
- Estrogen/progestogen Receptor
- Glucocorticoid Receptor
- GPR
- LHRH
- Opioid Receptor
- Oxytocin Receptor
- RAAS
- Reductase
- Thyroid hormone receptor(THR)
- 5-HT Receptor
- Adenosine Receptor
- Adiponectin receptor
- Adrenergic Receptor
- Amylin Receptor
- Annexin A
- Apelin receptor
- Arrestin
- Bombesin Receptor
- Bradykinin Receptor
- cAMP
- Cannabinoid Receptor
- CaSR
- CGRP Receptor
- cholecystokinin
- CRFR
- CXCR
- Dopamine Receptor
- EBI2/GPR183
- Endothelin Receptor
- GHSR
- Glucagon Receptor
- GNRH Receptor
- GPCR19
- GPR
- GRK
- GTPase
- Guanylate cyclase
- Hedgehog/Smoothened
- Histamine Receptor
- Kisspeptin
- Leukotriene Receptor
- LPA Receptor
- LPL Receptor
- Melanin-concentrating Hormone Receptor (MCHR)
- Melanocortin Receptor
- Melatonin Receptor
- Motilin Receptor
- Neurokinin receptor
- Neuropeptide W
- Neuropeptide Y Receptor
- Neurotensin Receptor
- Opioid Receptor
- OX Receptor
- Oxytocin Receptor
- P2Y Receptor
- PACAP
- PAFR
- Prostaglandin Receptor
- Protease-activated Receptor
- Ras
- RXFP receptor
- S1P Receptor
- SGLT
- Sigma receptor
- Somatostatin
- TSH Receptor
- Vasopressin Receptor
- AhR
- AIM2
- Antiviral
- Arginase
- Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor
- CCR
- CD38
- CD73
- Cell wall
- cGAS
- Complement System
- COX
- CXCR
- Cytokine release
- FKBP
- FLAP
- Galectin
- gp120/CD4
- Histamine Receptor
- IFNAR
- IL Receptor
- Immunology/Inflammation related
- Interleukin
- IRAK
- LTR
- MALT
- MRP
- MyD88
- NADPH-oxidase
- NO Synthase
- NOD
- NOD-like Receptor (NLR)
- NOS
- Nrf2
- PD-1/PD-L1
- PGE Synthase
- Prostaglandin Receptor
- Pyroptosis
- Reactive Oxygen Species
- ROS
- STING
- Thrombopoietin Receptor
- TLR
- EGFR
- HER
- JAK
- Pim
- STAT
- ERK
- JNK
- KLF
- KLF
- MAPK
- MEK
- MLK
- MNK
- p38 MAPK
- Raf
- Ras
- S6 Kinase
- TOPK
- ABC
- Anion Exchanger
- Aquaporin
- ATPase
- BCRP
- Calcium Channel
- CFTR
- Chloride channel
- CRM1
- GABA Receptor
- HCN Channel
- iGluR
- Monoamine Transporter
- Monocarboxylate transporter
- Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger
- Na-K-Cl cotransporter
- NPC1L1
- OAT
- OCT
- P2X Receptor
- P-gp
- Piezo Channel
- Potassium Channel
- Proton pump
- Sodium Channel
- TRP/TRPV Channel
- VDAC
- Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase
- aconitase
- Acyltransferase
- Adenosine deaminase
- AhR
- Amino Acids and Derivatives
- Aminopeptidase
- Amylase
- Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE)
- ATP Citrate Lyase
- Calcium Channel
- Carbonic Anhydrase
- Casein Kinase
- CETP
- CPT
- Decarboxylase
- Dehydrogenase
- DHFR
- Drug Metabolite
- Endogenous Metabolite
- Epoxide Hydrolase
- FAAH
- FABP
- Factor Xa
- Fatty Acid Synthase
- FXR
- Glucokinase
- Glucosidase
- Glutathione Peroxidase
- Glycosidase
- GSNOR
- hCE
- Hexokinase
- HIF/HIF Prolyl-Hydroxylase
- HMG-CoA Reductase
- HSP
- Hydrogenase
- Hydroxylase
- IDO
- Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase (IDO)
- Isocitrate Dehydrogenase (IDH)
- LDL
- Lipase
- Lipid
- Lipoxygenase
- Liver X Receptor
- MAGL
- MAO
- Mitochondrial Metabolism
- N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase
- NADPH
- NAMPT
- NEDD8
- Neprilysin
- NUDIX hydrolase
- P450
- PAI-1
- PDE
- Phosphatase
- Phospholipase
- Phosphorylase
- PKM
- PPAR
- Procollagen C Proteinase
- Prolyl Endopeptidase (PREP)
- RAR/RXR
- Reactive Oxygen Species
- Reductase
- Retinoid Receptor
- ROR
- Serine/threonin kinase
- SGK
- Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase (SCD)
- stilbene oxidase
- Taste receptor
- Thioredoxin
- Transaminase
- Transferase
- transporter
- UGT
- Vitamin
- Xanthine Oxidase
- Antibacterial
- Antibiotic
- Antifection
- Antifungal
- Anti-infection
- CCR
- GluCls
- HBV
- HCV Protease
- HIV Protease
- HSV
- Influenza Virus
- Integrase
- Parasite
- Reverse Transcriptase
- Ribosome
- RSV
- SARS-CoV
- Virus Protease
- 5-HT Receptor
- AAK1 (AP2 associated kinase 1)
- AChE
- AChR
- Adenosine Receptor
- Adenylyl cyclase
- Adrenergic Receptor
- BACE
- Beta Amyloid
- Beta-Secretase
- CaMK
- CGRP Receptor
- COX
- Dopamine Receptor
- FAAH
- GABA Receptor
- Gamma-secretase
- GluR
- GlyT
- Histamine Receptor
- Huntingtin
- iGluR
- Imidazoline Receptor
- MAO
- Melanocortin Receptor
- Monoamine Oxidase
- MT Receptor
- Neurokinin receptor
- Neuropeptide W
- Neuropeptide Y Receptor
- NMDAR
- NMU2R
- Norepinephrine
- Opioid Receptor
- OX Receptor
- P2X Receptor
- P2Y Receptor
- P-gp
- Serotonin Transporter
- IRAK
- IκB/IKK
- NF-κB
- NOD
- RANKL/RANK
- Reactive Oxygen Species
- RIP kinase
- advanced glycation end products
- CYP19A1
- Decarboxylase
- DprE1
- Fer/FerT kinase
- Others
- Platelet aggregation
- Progesterone Receptor
- Antioxidant
- CAT
- Free radical scavengers
- Glutathione reductase
- GPX
- GST
- Akt
- AMPK
- ATM/ATR
- DNA-PK
- GSK-3
- MELK
- mTOR
- PDK
- PI3K
- PI4K
- PTEN
- S6 Kinase
- SIK
- ATTECs
- AUTACs
- E3 Ligase Ligand-Linker Conjugate
- Ligand for E3 Ligase
- Ligands for Target Protein for PROTAC
- LYTACs
- Molecular Glues
- PROTAC Linker
- PROTACs
- SNIPERs
- Target Protein Ligand-Linker Conjugate
- Carboxypeptidase
- Caspase
- Cysteine Protease
- DPP-4
- Gamma-secretase
- Glutaminase
- HCV Protease
- HIV Protease
- MMP
- Prolyl Endopeptidase (PREP)
- Protease
- Proteasome
- Serine Protease
- Thrombin
- Tyrosinase
- Casein Kinase
- Gamma-secretase
- GSK-3
- Hedgehog/Smoothened
- Hippo pathway
- JAK
- Porcupine
- ROCK
- Smo
- STAT
- Stemness kinase
- TGF-beta/Smad
- Wnt/beta-catenin
- YAP
- ACK
- ALK
- Bcr-Abl
- BTK
- c-Fms
- c-Kit
- c-Met/HGFR
- c-RET
- CSF-1R
- Discoidin Domain Receptor (DDR)
- DYRK
- EGFR
- Ephrin Receptor
- FAK
- FGFR
- FLT
- Hck
- HER
- IGF-1R
- PDGFR
- PKA
- PYK2
- ROS Kinase
- Src
- Syk
- TAM Receptor
- Tie-2
- Trk receptor
- Tyrosine Kinases
- VEGFR
- DUB
- E1/E2/E3 Enzyme
- p97
- Proteasome
- PROTAC-Linker Conjugates for PAC
- Drug-Linker Conjugates for ADC
- Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs)
- ADC Linker
- ADC Cytotoxin
- ADC Antibody
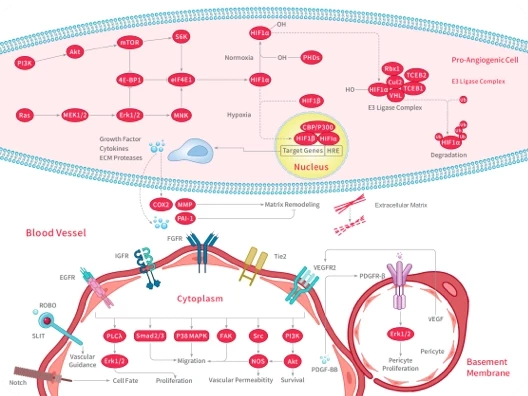
- General Bioactive Libraries
- Approved / Repurposing
- Characteristic Bioactive Libraries
- Disease Focused
- Target / Pathway Focused
- Natural Product Derivatives Libraries
- Natural Product Library for HTS
- Characteristic Natural Product Libraries
- TCM Natural Product Library
- Activity-classified Natural Product Library
- Structure-classified Natural Product Library
- Characteristic Fragment Libraries
- General Fragment Libraries
- Compound Libraries for HTS/HCS
- Tumor
- Anti-infective
- Cardiovascular disease
- Development and reproduction
- Digestive disorders
- Inflammation and immunity
- Metabolic diseases
- Neurological disorders
- Other Fields

- Alangiaceae
- Aquifoliaceae
- Cephalotaxaceae
- Costaceae
- Daphniphyllaceae
- Dioscoreaceae
- Eucommiaceae
- Ginkgoaceae
- Hippocastanaceae
- Illiciaceae
- Lycopodiaceae
- Moringaceae
- Myricaceae
- Myristicaceae
- Nelumbonaceae
- Nothofagaceae
- Nyssaceae
- Orobanchaceae
- Paeoniaceae
- Piperaceae
- Podocarpaceae
- Pteridaceae
- Resedaceae
- Sapindaceae
- Schisandraceae
- Stemonaceae
- Theaceae
- Other
- Alkaloids
- Coumarins
- Flavonoids
- Lignans
- Others
- Phenols
- Phenylpropanoids
- Quinones
- Saccharides and Glycosides
- Steroids
- Terpenoids

- Hematologic Malignancies Target Proteins
- Solid Tumors Target Proteins
- B Cell CD Proteins
- Cell Activation CD Proteins
- Cell Adhesion CD Proteins
- Cytokine Receptor CD Proteins
- Endothelial Cell CD Proteins
- Myeloid Cell CD Proteins
- NK/Non-lineage Cell CD Proteins
- Other CD Proteins
- Platelet CD Proteins
- T Cell CD Proteins
- Cytokines
- Epidermal Growth Factor Family, EGFs
- Growth Factors
- Others
- Hydrolases,EC 3
- Isomerases,EC 5
- Ligases or Synthetases,EC 6
- Lyases,EC 4
- Oxidoreductases,EC 1
- Transferases,EC 2
- Translocases,EC 7
- Butyrophilins
- Co-inhibitory Immune Checkpoint Proteins
- Co-stimulatory Immune Checkpoint Proteins
- Cell Adhesion Receptors
- Cytokines and Growth Factor Receptors
- Enzyme-Linked Receptors
- Fc Receptors
- G Protein-Coupled Receptors, GPCRs
- Ion Channel-Linked Receptors
- Nuclear Receptors
- Receptor Serine/Threonine Kinases
- Receptor Tyrosine Kinases
- Others
- Coronavirus (CoV) Proteins
- DENV Proteins
- EBOV Proteins
- HBV Proteins
- HCV Proteins
- HIV Proteins
- Influenza Proteins
- RSV Proteins
- Others

- Molecular Docking
- Virtual Screening
- Biomolecular Interaction
- Custom Synthesis
- AI-driven Ultra High-throughput Virtual Screening

CD Proteins
The term CD (Cluster of Differentiation) translates to clusters or groups of differentiation, also known as leukocyte differentiation antigens. These refer to cell surface markers that appear or disappear on various lineages of white blood cells during different stages of normal differentiation, maturation, and activation processes. They are mostly glycoprotein molecules. Physiologically, CD molecules often serve as important receptors or ligands on cells and as cellular markers for immune antigen recognition. However, some CD proteins are unrelated to cell signaling, but play roles in cell adhesion, activation, or inhibition.
- TOP
 Feedback
Feedback Hello! How can I help you today?
Hello! How can I help you today? 

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.
