- Remove All

NEWS | 28 June 2024
By TargetMol

Cisplatin (CDDP), chemically known as cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II), has the molecular formula PtCl₂(NH₃)₂. Cisplatin features a divalent platinum ion as the central ion, coordinated in a square planar configuration with four dsp² hybrid orbitals of platinum acting as empty orbitals. These orbitals accept lone pairs of electrons provided by two ammonia molecules and two chloride ions, forming a square planar coordination complex. In this molecular structure, the two ammonia molecules and the two chloride ions are positioned on the same side of the square plane, creating a cis configuration. This cis configuration is crucial for cisplatin's anticancer activity[1].
Mechanism of Action
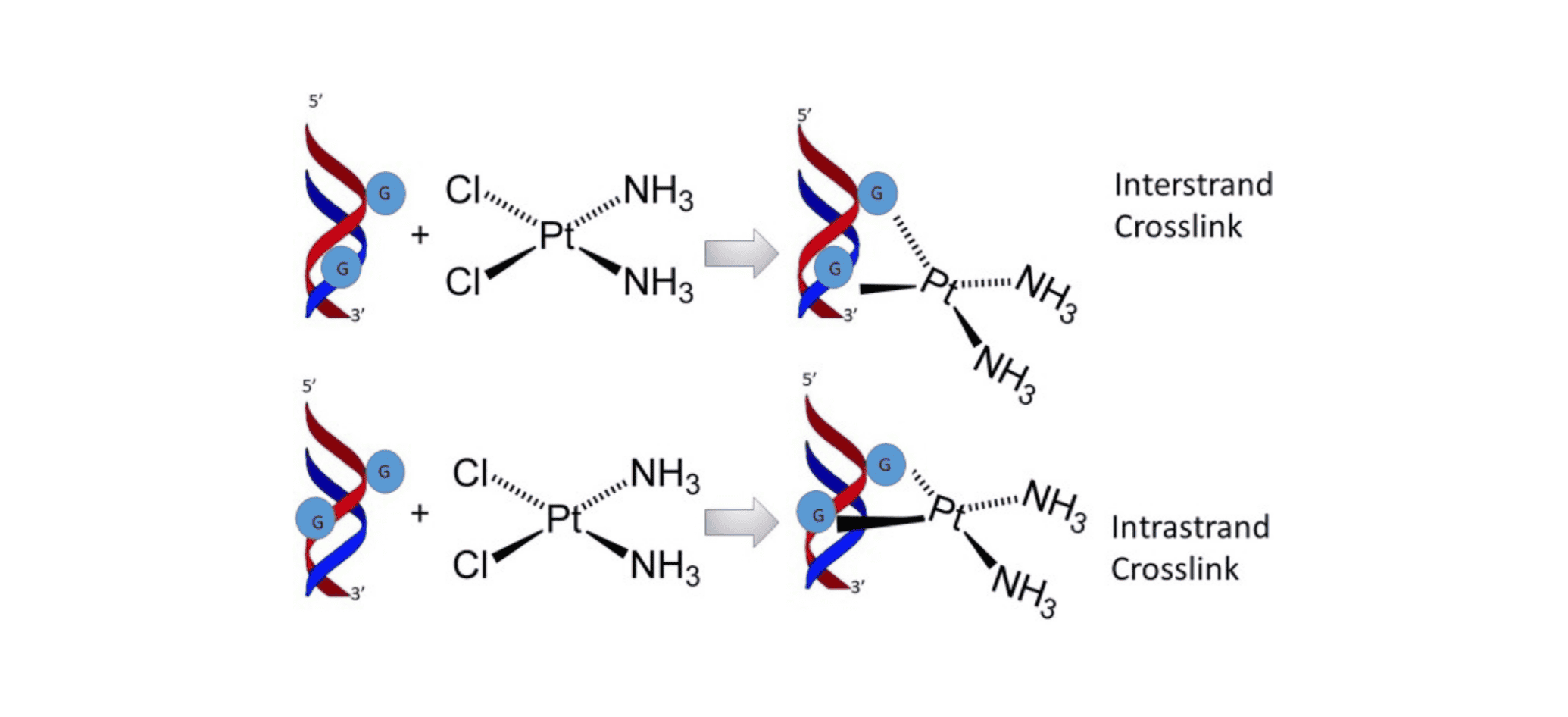
Cisplatin is a widely used chemotherapy drug for treating various forms of cancer. This is mainly due to its ability to crosslink DNA purine bases, thereby interfering with the DNA repair mechanisms in cancer cells. Cisplatin is chemically inert and must be activated through hydrolysis. When chloride ions are replaced by water molecules, a highly electrophilic reagent is produced. The electrophilic form of cisplatin tends to bind with endogenous nucleophiles, such as methionine, reduced glutathione (GSH), and metallothionein, forming interstrand and intrastrand crosslinks that are resistant to DNA repair mechanisms. Cisplatin readily forms 1, 2-[Pt(NH3)2]-d(GpG) intrastrand crosslink products, which cause the DNA to maintain an unwound state or bend, reducing the stability of DNA and ultimately rendering it non-functional.
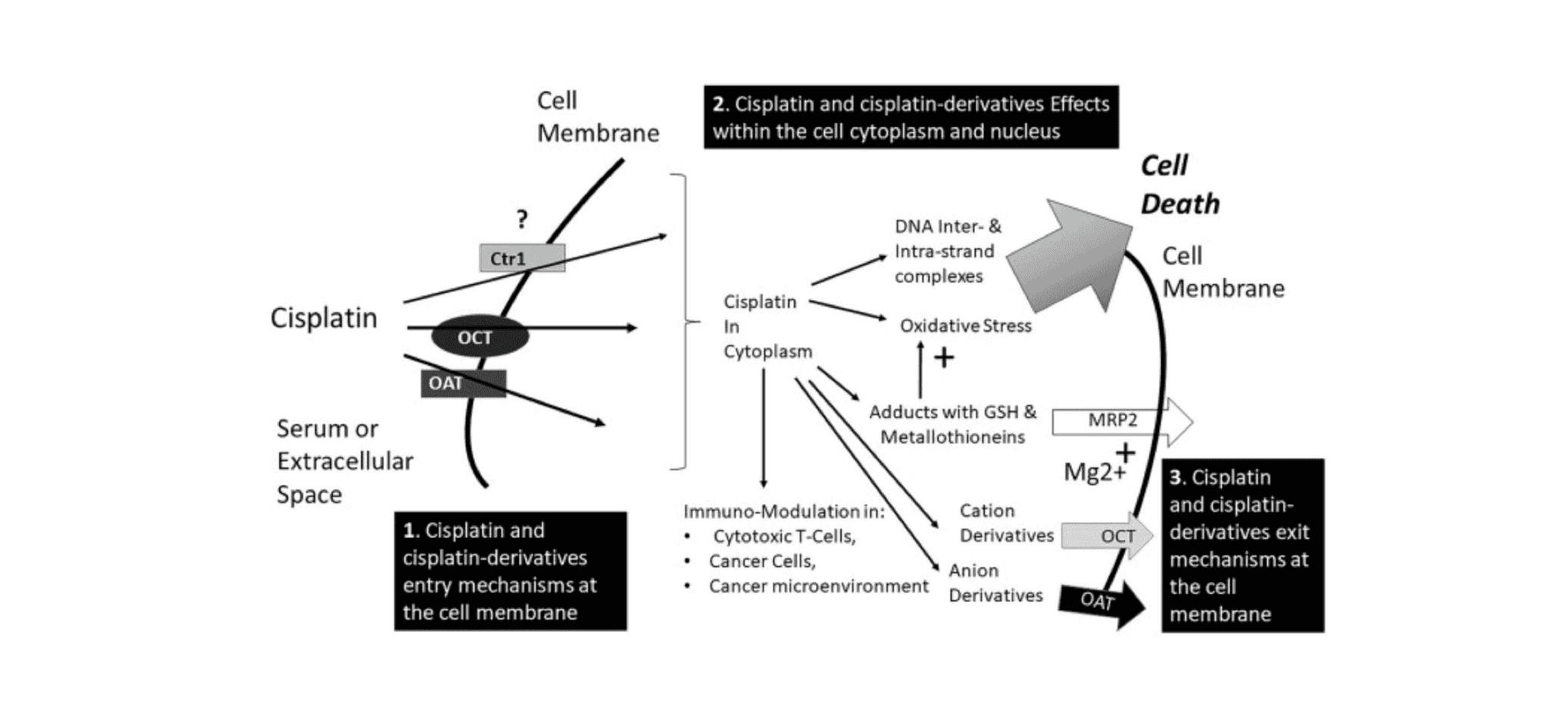
Cisplatin-induced DNA damage activates the tumor suppressor gene p53. When the damaged DNA cannot be repaired, the activation of p53 triggers caspase-mediated apoptosis, leading to cell death[2]. Studies have shown that cisplatin can also induce the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cells, thereby triggering cell death. Furthermore, the concentration of cisplatin and the duration of its action directly affect ROS formation[3].
Application
In 1978, after clinical trials, cisplatin was approved by the FDA as the first platinum-based anticancer drug for clinical use. Today, cisplatin is widely used to treat a range of human tumors, including ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, testicular cancer, lung cancer, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, esophageal cancer, malignant lymphoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, thyroid cancer, and osteosarcoma.
References
[1] Romani AMP. Cisplatin in cancer treatment. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Dec;206:115323. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115323. Epub 2022 Nov 8. PMID: 36368406.
[2] Sun CY, Zhang QY, Zheng GJ, Feng B. Phytochemicals: Current strategy to sensitize cancer cells to cisplatin. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Feb;110:518-527. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.010. Epub 2018 Dec 7. PMID: 30530287.
[3]Brozovic A. ; Ambriovic-Ristov A. ; Osmak M. Crit. Rev. Toxical. 2010, 40 (4), 347.DOI:10.3109/10408441003601836

An essential round-up of science news, opinion and analysis, delivered to your inbox every weekday.

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.