- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Shopping Cart
Filter
5-HT Receptor
(622)
Adenosine Receptor
(128)
Adiponectin Receptor
(5)
Adrenergic Receptor
(385)
Amylin Receptor
(5)
Annexin A
(8)
Apelin receptor
(14)
Arrestin
(15)
Bombesin Receptor
(15)
Bradykinin Receptor
(24)
CCR
(83)
CGRP Receptor
(23)
CRFR
(18)
CXCR
(78)
CaSR
(22)
Cannabinoid Receptor
(126)
Cholecystokinin Receptor
(34)
Dopamine Receptor
(334)
EBI2/GPR183
(3)
Endothelin Receptor
(39)
GHSR
(20)
GNRH Receptor
(27)
GPCR19
(16)
GPR
(151)
GRK
(13)
GTPase
(19)
Glucagon Receptor
(69)
Guanylate cyclase
(27)
Hedgehog/Smoothened
(40)
Histamine Receptor
(253)
Kisspeptin
(4)
Kras
(33)
LPA Receptor
(24)
LPL Receptor
(51)
Leukotriene Receptor
(38)
MRGPR
(6)
Melanin-concentrating Hormone Receptor (MCHR)
(11)
Melanocortin Receptor
(42)
Melatonin Receptor
(13)
Motilin Receptor
(3)
Neurokinin receptor
(72)
Neuropeptide W
(1)
Neuropeptide Y Receptor
(56)
Neurotensin Receptor
(25)
OX Receptor
(26)
Opioid Receptor
(168)
Oxytocin Receptor
(17)
P2Y Receptor
(37)
PACAP
(10)
PAFR
(41)
Prostaglandin Receptor
(190)
Protease-activated Receptor
(39)
RXFP receptor
(5)
Ras
(126)
S1P Receptor
(58)
SGLT
(30)
Sigma receptor
(56)
Somatostatin
(21)
TSH Receptor
(10)
Vasopressin Receptor
(33)
cAMP
(43)
AIM2
(4)
AhR
(27)
Antiviral
(140)
Arginase
(13)
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor
(30)
BCL6
(1)
CCR
(83)
CD38
(9)
CD73
(15)
COX
(400)
CXCR
(78)
Cell wall
(7)
Complement System
(53)
FKBP
(5)
FLAP
(12)
Galectin
(10)
Histamine Receptor
(253)
IFNAR
(22)
IKZF
(1)
IL Receptor
(244)
IRAK
(35)
Immunology/Inflammation related
(95)
Interleukin
(73)
LAG-3
(7)
LTR
(40)
MALT
(7)
MRP
(27)
Mucin
(3)
MyD88
(8)
NADPH-oxidase
(34)
NO Synthase
(146)
NOD
(42)
NOD-like Receptor (NLR)
(69)
NOS
(124)
Nrf2
(91)
PD-1/PD-L1
(97)
PGE Synthase
(20)
PSMA
(15)
Prostaglandin Receptor
(190)
Pyroptosis
(13)
ROS
(154)
Reactive Oxygen Species
(257)
STING
(45)
TLR
(109)
TROP2
(4)
Thrombopoietin Receptor
(4)
cGAS
(9)
gp120/CD4
(7)
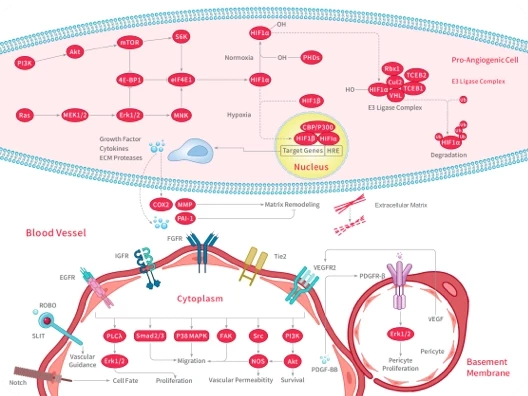
Prostaglandin Receptor
Prostaglandin receptors or prostanoid receptors represent a sub-class of cell surface membrane receptors that are regarded as the primary receptors for one or more of the classical, naturally occurring prostanoids viz., prostaglandin D2, , PGE2, PGF2alpha, prostacyclin (PGI2), thromboxane A2 (TXA2), and PGH2.[1] They are named based on the prostanoid to which they preferentially bind and respond, e.g. the receptor responsive to PGI2 at lower concentrations than any other prostanoid is named the Prostacyclin receptor (IP). One exception to this rule is the receptor for thromboxane A2 (TP) which binds and responds to PGH2 and TXA2 equally well.
Cis-N-Feruloyltyramine
TN366980510-09-4In house
Cis-N-Feruloyltyramine is a naturally occurring compound found in various plants that shows cytotoxicity against the P-388 cancer cell line. Cis-N-Feruloyltyramine is an inhibitor of in vitro prostaglandin (PG) synthesis.
- $137
Size
QTY
Aligeron
T3661970713-45-0In house
Aligeron, a non-selective prostaglandin (PG) antagonist, inhibits PGF2α- and PGE2-induced blood pressure decreases in cats and can prevent PGF2α-induced diarrhea in mice and PGE2-induced paw edema in rats. Additionally, Aligeron is recognized for its antioxidant-protective effect against vascular complications.
- $700
Size
QTY
Prostaglandin E1 Cited
Cited
T1626745-65-3
Prostaglandin E1 (Alprostadil) is the naturally occurring prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) which displays a variety of pharmacologic actions. Prostaglandin E1 is a potent vasodilator agent that increases peripheral blood flow, inhibits platelet aggregation, and induces bronchodilation. Used in the treatment of erectile dysfunction, this agent produces corporal smooth muscle relaxation by binding to PGE receptors, resulting in the activation of adenylate cyclase and the subsequent accumulation of 3'5'-cAMP.
- $30
Size
QTY
sphondin Cited
Cited
T5758483-66-9
Sphondin has anticonvulsant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-proliferative activities, it possessed an inhibitory effect on IL-1beta-induced increase in the level of COX-2 protein and PGE(2) release in A549 cells.
- $113
Size
QTY
NTP42 Cited
Cited
T122682055599-51-2
NTP42 is an antagonist of thromboxane A2 (TXA2) receptor(IC50 of 3.278 nM)
- $57
Size
QTY
TP-16
T625252332972-26-4In house
TP-16 is a novel potent and selective EP4 antagonist that blocks the function of IMCs and enhances cytotoxic T cell-mediated tumor elimination in vivo.
- $462

Size
QTY
Laropiprant
T15712571170-77-9
Laropiprant (MK-0524) is a potent and selective antagonist of prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) receptor (DP) such as and DP DP1 receptor(Ki = 0.57 nM) and TP Receptor(Ki = 2.95 nM).
- $32
Size
QTY
Platycodin D Cited
Cited
T388958479-68-8
Platycodin D may stimulate TNF-α synthesis or inhibit degradation of TNF-α mRNA. Platycodin D (10 30 μM) suppresses prostaglandin E2 production in rat peritoneal macrophages stimulated by the protein kinase C activator 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol 13-acetate (TPA). Platycodin D and D3 are useful as expectorant agents in the treatment of various airway diseases, they can increase mucin release from rat and hamster tracheal surface epithelial cell culture and also from intact rat trachea upon nebulization.
- $52
Size
QTY
L-161982
T15681147776-06-5In house
L-161982 is a selective EP4 receptor antagonist that inhibits PGE2-induced ERK phosphorylation and cell proliferation in HCA-7 cells and alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice.
- $72
Size
QTY
Rutin
 Cited
Cited
T0795153-18-4
Rutin (Quercetin 3-O-rutinoside), a flavonoid, has a variety of biological activities including antiallergic, anti-inflammatory, antiproliferative, and anticarcinogenic properties.
- $36
Size
QTY
Taraxasterol
T37701059-14-9
Taraxasterol (Taraxasterin) is compound with anti-inflammatory activity.
- $71
Size
QTY
Tiopinac
T1710161220-69-7In house
Tiopinac (RS 40974) has anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity, and exhibits anti-flammatory activity in adrenalectomized rats.
- $208
Size
QTY
Furprofen
T1134066318-17-0In house
Furprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent that inhibits prostate (PGE) synthesis and is used in the study of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
- $42

Size
QTY
mPGES-1 Inhibitor-1
T280891381846-21-4In house
mPGES-1 Inhibitor-1 is a novel selective inhibitor of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1) with anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity for the study of acute liver injury.
- $196
Size
QTY
ONO-8713
T63667459411-08-6In house
ONO-8713 is a selective prostaglandin E receptor subtype EP1 antagonist used to study diseases of the biblical system and metabolism-related diseases.
- $397
Size
QTY
RO1138452
T4436221529-58-4
RO1138452 (CAY10441) is a selective and orally bioavailable antagonist of prostacyclin receptor (pKi: 8.3). It antagonizes the carbaprostacyclin-induced activation of human neuroblastoma adenylate cyclase, blocking cyclic AMP accumulation in a dose-dependent manner. Likewise, it inhibits the binding of tritiated iloprost to rodent neuroblastoma cells with a Ki of about 1.5 nM. At levels between 2-20 mg kg in rats, CAY10441 shows significant analgesic activity in standard antinociceptive assays [1].
- $44
Size
QTY
Octimibate
T2456789838-96-0In house
Octimibate (Octimibato) is a non-prostaglandin platelet aggregation inhibitor and cyclic prostaglandin agonist.Octimibate is used in the treatment of cardiovascular disease and can be used to study atherosclerosis and thrombosis.
- $143
Size
QTY
DG-041
T15108861238-35-9
DG-041 is an antagonist of high-affinity EP3 receptor (IC50s: 4.6 nM and 8.1 nM in the binding and FLIPR assay, respectively). DG-041 inhibits PGE2 facilitation of platelet aggregation and has the blood-brain barrier permeability.
- $43
Size
QTY
Ginsenoside Ro
T391534367-04-9
Ginsenoside Ro (Chikusetsusaponin V) can reduce TXA2 production, weakly reduce COX-1 and TXAS activities, and has antiplatelet effects as a Ca2+ antagonist with an IC50 of 155 μM.
- $64
Size
QTY
RO3244794
T69360361457-01-4
RO3244794 is a selective prostacyclin (IP) receptor antagonist that can be used to study liver injury.
- $293
Size
QTY
BAY-6672
T397602247517-53-7
BAY-6672 is a selective human prostaglandin F (FP) receptor antagonist that is highly potent (IC50=11 nM), orally available and well permeable. It exerts antifibrotic effects by inhibiting prostaglandin F2α (PGF₂α) activity through antagonizing the FP receptor, and has in vivo efficacy in animal models of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).
- $196
Size
QTY
Gestonorone Capronate
T137031253-28-7
Gestonorone Capronate is a progesterone used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia and endometrial cancer.
- $148
Size
QTY
Latanoprost Cited
Cited
T2528130209-82-4
Latanoprost (Xalatan) is a prostaglandin F2alpha analogue and a prostanoid selective FP receptor agonist with an ocular hypertensive effect.
- $39
Size
QTY
Beta-Hydroxyisovalerylshikonin
TN14407415-78-3
Beta-Hydroxyisovalerylshikonin is an inhibitor of protein-tyrosine kinases such as v-Src and EGFR, and has been shown to induce apoptosis in several human tumor cell lines. Beta-Hydroxyisovalerylshikonin significantly decreased viability of HCT116 cells (IC50 values = 30.9 μg mL).
- $139
Size
QTY
Bimatoprost
T2538155206-00-1
Bimatoprost (AGN 192024) is a cloprostenol-derived amide that is used as an antihypertensive agent in the treatment of open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension.
- $30
Size
QTY
Evodiamine
T2868518-17-2
Evodiamine (d-Evodiamine) is an alkaloid isolated from the fruit of daylily and has a variety of biological activities including anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity and anti-tumor.
- $42
Size
QTY
Treprostinil
T515081846-19-7
Treprostinil (Orenitram) is a potent DP1, IP and EP2 agonist (EC50: 0.6 1.9 6.2 nM).
- $30
Size
QTY
Agnuside
T386811027-63-7
Agnuside (chasteberry oil) inhibits COX-2 (IC50: 0.026 mg ml) but exhibits less than 10% inhibition of COX-1 at this concentration. It also inhibits 46.3, 66.8, and 82.1% of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) ATPase activity at concentrations of 5, 25, and 100 μM, respectively.
- $39
Size
QTY
Afzelin
TN1362482-39-3
Afzelin (Kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside) exhibits several cellular activities such as DNA-protective, antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and UV-absorbing properties, potentially protecting human skin from UVB-induced damage through a combination of UV-absorbing and cellular actions. Afzelin mitigates mitochondrial damage, promotes mitochondrial biogenesis, and reduces levels of mitophagy-related proteins, parkin and PTEN-induced putative kinase 1.
- $41
Size
QTY
Isbogrel
T2763089667-40-3In house
Isbogrel (CV4151) is a small molecule thromboxane A2 synthase (TXA2 synthase) inhibitor that can be used to study cardiac arrhythmias, transient ischemic attacks and thrombosis.
- $350
Size
QTY
AMG-009
T142111027847-67-1
AMG-009 is a selective and potent dual antagonist of CRTH2 and DP, with an IC50 value of 3 nM for CRTH2 and 12 nM for DP receptors.
- $41
Size
QTY
Grapiprant
TQ0292415903-37-6
Grapiprant (AAT-007) is a selective EP4 receptor antagonist. Grapiprant displaces [3H]-PGE2 (1 nM) binding to dog recombinant EP4 receptor (IC50: 35 nM, Ki: 24 nM).
- $30
Size
QTY
Tranilast Cited
Cited
T269053902-12-8
Tranilast (SB 252218), an antiallergic drug, suppresses lipid mediator and cytokine release from inflammatory cells, therefore utilized in the treatment of allergic disorders.
- $36
Size
QTY
Treprostinil diethanolamine
T63349830354-48-8
Treprostinil diethanolamine (UT-15C) is a potent agonist of EP2, DP1, and IP, with values of 3.6, 4.4, and 32.1 nM for EP2, DP1, and IP, respectively, and 212, 826, 2505, and 4680 nM for EP1, EP4, EP3, and FPKi, respectively. Treprostinil diethanolamine contributes to the upregulation of cAMP, maintaining vascular homeostasis and causing vasodilation in human pulmonary arteries.
- $68
Size
QTY
Rebamipide
T156290098-04-7
Rebamipide (OPC12759) is a quinolinone derivative with anti-ulcer and anti-inflammatory activities. Rebamipide induces cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2) synthesis which results in an increase in endogenous prostaglandin synthesis in the gastric mucosa. This agent also inhibits H. pylori-induced production of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha and subsequent inflammation of the gastric mucosa. In addition, rebamipide scavenges oxygen-derived free radicals that potentially cause mucosal injury, and stimulates prostaglandin EP4 receptor gene expression followed by mucous secretion, thereby enhancing the gastric mucosal defense.
- $45
Size
QTY
Vidupiprant
T172321169483-24-2
Vidupiprant (AMG 853) is an effective dual antagonist of CRTH2 and prostanoid D receptor with IC50s of 8 nM and 35 nM in human plasma. Vidupiprant can be used in studies about the treatment of asthma.
- $61
Size
QTY
Darbufelone
T10960139226-28-1In house
Darbufelone (CI-1004) is a non-competitive dual inhibitor of PGF2α and LTB4. Dabfilon effectively inhibits PGHS-2 with a Ki of 10 μM and IC50s of 0.19 μM and 20 μM for PGHS-2 and PGHS-1.
- $37
Size
QTY
L-798106
T15689244101-02-8
L-798106 (CM9) is a selective and potent prostaglandin-like EP3 receptor antagonist that inhibits EP4, EP1, and EP2 receptors, suppresses levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in atherosclerosis, and attenuates PGE2-induced cough.
- $41
Size
QTY
Embelin Cited
Cited
T6485550-24-3
Embelin (Embelic acid), isolated from the Japanese Ardisia herb, is an inhibitor of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (IC50: 4.1 uM).
- $50
Size
QTY
Travoprost
T5841157283-68-6
Travoprost (Fluprostenol isopropyl ester) is used to treat glaucoma and ocular hypertension,is a potent and selective FP prostaglandin receptor agonist.
- $40
Size
QTY
3-O-Acetyl-α-boswellic acid
TN125789913-60-0
3-O-Acetyl-α-boswellic acid (α-Boswellic acid acetate) exhibits potent anti-inflammatory activity.
- $40
Size
QTY
PGD2-IN-1
T4624885066-67-1In house
PGD2-IN-1 (PGD2-inhibitor) is an effective DP receptor antagonist (IC50:0.3 nM), a compound that can inhibit prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) signaling. PGD2-IN-1 specifically targets and regulates the activity of PGD2 receptors or enzymes involved IN PGD2 synthesis or metabolism.
- $64
Size
QTY
Selexipag
T3216475086-01-2
Selexipag (ACT-293987)(NS-304) is prostacyclin receptor agonist that causes vasodilation in pulmonary vasculature and is used in the therapy of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH).
- $42
Size
QTY
EP4 receptor antagonist 1
T112112287259-07-6
EP4 Receptor Antagonist 1 is a highly potent and selective competitive prostanoid EP4 receptor antagonist, effective for cancer immunotherapy. It inhibits both human and mouse EP4 receptors with IC50 values of 6.1 nM and 16.2 nM, respectively, while displaying minimal activity (IC50s >10 μM) against human EP1, EP2, and EP3 receptors.
- $107
Size
QTY
ETHYL 2-AMINO-4-METHYL-5-PHENYLTHIOPHENE-3-CARBOXYLATE
T86034815-38-7
ETHYL 2-AMINO-4-METHYL-5-PHENYLTHIOPHENE-3-CARBOXYLATE targets the prostaglandin E2 receptor EP2 subtype (human)
- $30
Size
QTY
Darbufelone mesylate
T10960L139340-56-0In house
Darbufelone mesylate (CI-1004 mesylate) inhibited PGF2α and LTB4 in cells and demonstrated IC50 values of 0.19 μM for PGHS-2 and 20 μM for PGHS-1.
- $48
Size
QTY
Vedaprofen
T3668371109-09-6In house
Vedaprofen (PM 150) inhibits COX-1 and reduces prostaglandin H2 synthesis with anti-inflammatory activities. Vedaprofen is an inhibitor of Escherichia coli sliding clamp with the IC50 of 222 μM and Ki of 131 μM.
- $49
Size
QTY
PF-9184
T217381221971-47-6In house
PF-9184 is a potent and selective inhibitor of human microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1) with an IC50 of 16.5 nM, and it inhibits IL-1β-induced PGE2 synthesis in vitro.
- $30
Size
QTY
Go to page 1
Page of 4

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.